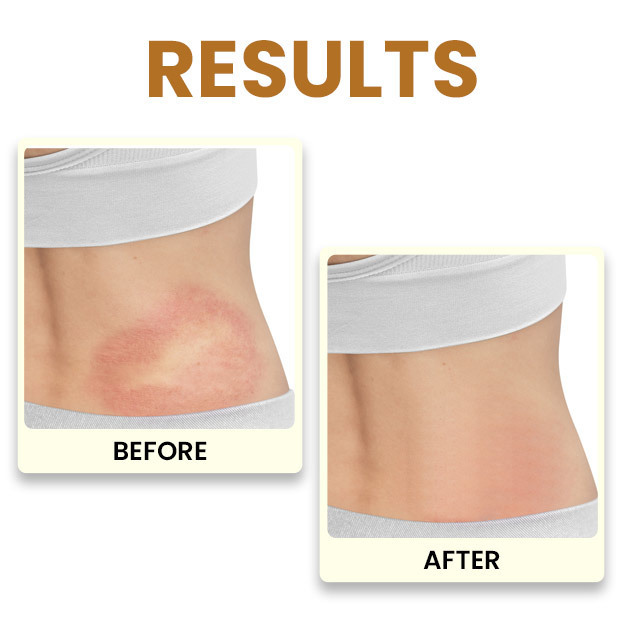
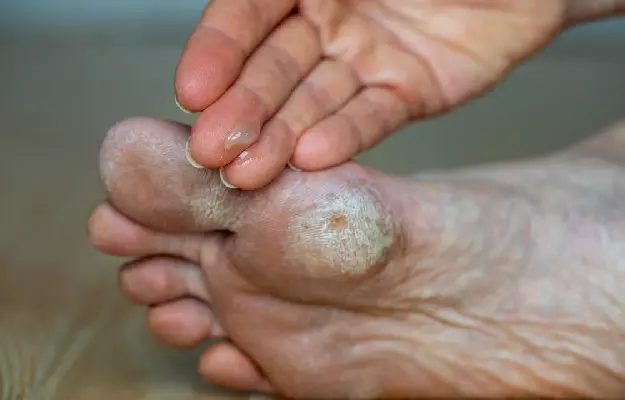
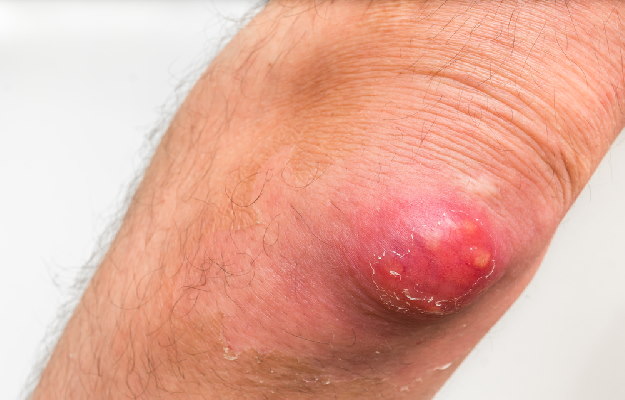
Hyperkeratosis is a skin condition that occurs when a person's skin becomes thicker than normal in certain places such as calluses, corns, eczema and more. Keratin is a tough, fibrous protein found in nails, hair, and skin. The body produces more keratin than needed as a result of inflammation, as a protective response to pressure, or as a result of a genetic condition. Most forms of hyperkeratosis can be treated with preventive measures and medication.
In general terms, hyperkeratosis means thickening of the outer layer of the skin. This layer is made of a protein called keratin. Many different skin conditions cause keratin to grow excessively.
Certain types of hyperkeratosis are hereditary and are present at birth. Some other types of hyperkeratosis may be early symptoms of skin cancer that develops later.
Read more - (Skin Infections symptoms, causes, treatment)
To remove pimples and itching from the skin, definitely use nimbadi churna by myUpchar.