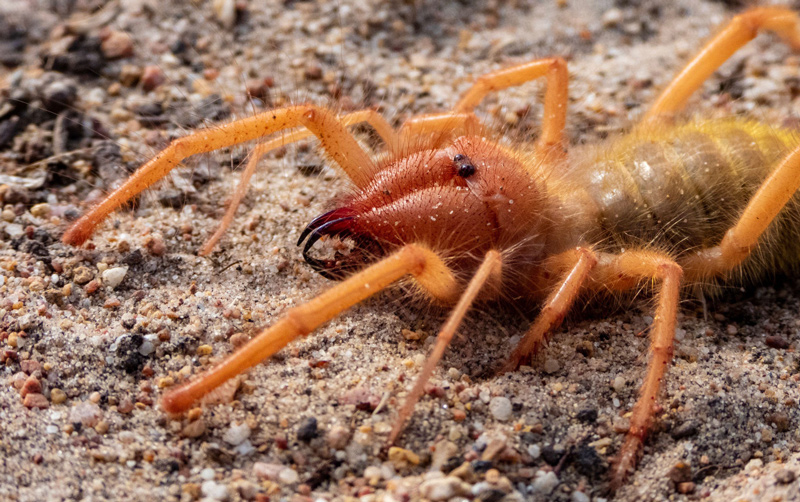

A new study has unveiled the long-standing mysteries surrounding camel spiders (Solifugae). This pioneering research marks a major milestone by establishing the very first comprehensive molecular tree, or phylogeny, of this enigmatic arachnid order, shedding light on their evolutionary history and relationships. By harnessing advanced sequencing technologies and a unique genetic dataset, the study has overcome past challenges in distinguishing and understanding the evolution of these remarkable creatures. The research not only reclassifies camel spiders into two new groups but also highlights the significance of modern genomic techniques in uncovering the secrets of enigmatic organisms, ultimately deepening our appreciation for biodiversity and evolutionary science.
September 14, 2023 – In a new study led by the laboratories of Prof. Prashant Sharma of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, and Dr. Efrat Gavish-Regev of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, a team of researchers has uncovered the mysteries surrounding camel spiders (Solifugae), by successfully establishing the first-ever comprehensive molecular tree (phylogeny) of this enigmatic arachnid order. Their findings, based on advanced sequencing technologies (UCE) and a novel dataset, have provided invaluable insights into the evolutionary history and relationships of camel spiders.
Camel Spiders, often referred to as “neglected arachnid cousins,” have long been a subject of fascination due to their remarkable features such as aggression, exceptional running speed, and adaptation to arid environments. Despite their notoriety, the lack of a higher-level phylogeny has left many questions unanswered about the evolutionary history of these intriguing creatures.
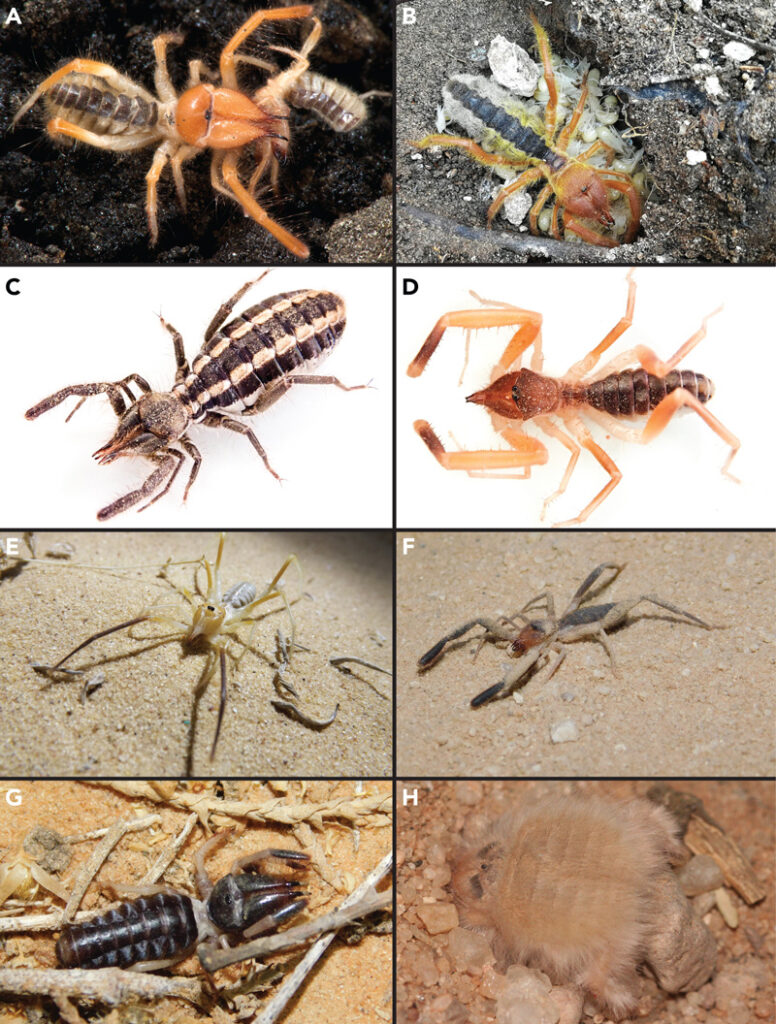

In the past, it was hard to study camel spiders because we couldn’t easily tell them apart based on their phenotype. Until recently, the phylogeny of only one family out of the 12 recent families of camel spiders was studied using their genes (the parts of their cells that carry information), mainly because many historical specimens are stored for decades in collections around the world in conditions that were damaging their DNA, and made it useless for genomic study.
But now, Prof. Sharma, Dr. Gavish-Regev and their collaborators have used advanced techniques to look at specific parts of the genome that are conserved in all camel spiders, and the regions around them that had been changed during evolution. Spearheaded by Dr. Siddharth Kulkarni, a postdoctoral researcher in Madison, the novel method they used can also take advantage of historical material and leverage fragmented DNA for genetic analysis. This allowed them to learn more about all the different families of camel spiders and their relationships with each other.
This research helped create a clear higher-level tree for camel spiders, showing how they are related to each other in terms of their evolution. They discovered that there are two main groups of camel spiders in the Americas, and they are part of a bigger group of camel spiders that started evolving in tropical regions long time ago.
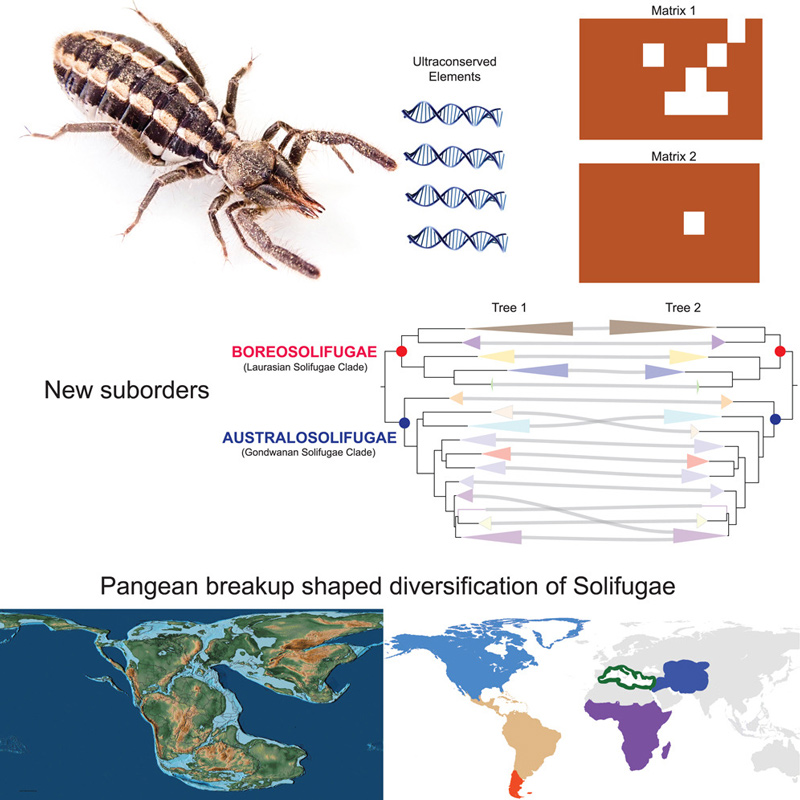
By looking at ancient evidence, like fossils, the researchers figured out that camel spiders began evolving around 250-300 million years ago during the Permian period. Most of these camel spider families were already different from each other before a major extinction event around 66 million years ago, which is when many species, including the dinosaurs, disappeared. This suggests that the breakup of continents had a big impact on how camel spiders evolved.
The study has made an important discovery in how we classify camel spiders. They suggest creating two new groups: one for camel spiders from Laurasia (a landmass in the northern hemisphere) called “Boreosolifugae” and another for those from Gondwana (a landmass in the southern hemisphere) called “Australosolifugae.” They have good reasons to do this based on the physical characteristics of these arachnids and where they live. This finding is significant because it changes how we organize and understand camel spiders in the big picture of their higher-level tree.
Dr. Efrat Gavish-Regev, expressed her excitement about the research, stating, “Our work has finally brought camel spiders out of the shadows and into the light of phylogenomic analysis. We now have a better picture of their evolutionary history and relationships, and our proposed suborders provide a solid framework for future research in this fascinating field.”

This study not only fills a significant gap in the understanding of arachnid evolution but also showcases the power of modern genomic techniques in uncovering the mysteries of enigmatic organisms living in challenging environments. The findings are poised to stimulate further research into Solifugae and deepen our appreciation for the biodiversity of our planet.
The study, titled “Neglected no longer: Phylogenomic resolution of higher-level relationships in Solifugae” has been published in the iScience and can be found at https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(23)01761-3.
Research Team: Siddharth S. Kulkarni-1, Hugh G. Steiner-1, Erika L. Garcia-2, Hernán Iuri-3, R. Ryan Jones-3, Jesús A. Ballesteros-4, Guilherme Gainett-1, Matthew R. Graham-5, Danilo Harms-6, Robin Lyle-7, Andrés A. Ojanguren-Affilastro-3, Carlos E. Santibañez-López-8, Gustavo Silva de Miranda-9, Paula E. Cushing-2, Efrat Gavish-Regev, Prashant P. Sharma-1
Institutions:
- Department of Integrative Biology, The University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Department of Zoology, Denver Museum of Nature & Science
- División de Aracnología, Museo Argentino de Ciencias Naturales “Bernardino Rivadavia”, Buenos Aires
- Department of Biology, Kean University
- Department of Biology, Eastern Connecticut State University
- Museum of Nature Hamburg – Zoology, Department of Invertebrates, Leibniz Institute for the Analysis of Biodiversity Change, Hamburg
- Biosystematics: Arachnology, ARC—Plant Health and Protection, Pretoria
- Department of Biology, Western Connecticut State University, Danbury
- Department of Entomology, National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution
- 10-The National Natural History Collections, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
About the National Natural History Collections
The National Natural History Collections at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem are the most extensive biological collections of the Middle East. In addition to serving as a physical documentary of the regional natural history, the collections provide research material for studies in evolution, ecology, taxonomy, systematics, biodiversity, nature conservation, agriculture, wildlife forensics, history, and more. Learn more about the National Collections: https://en-nnhc.huji.ac.il